How Scale’s Supplier Master Table Redefines ‘Know Your Supplier’
Scale’s Know Your Supplier (KYS) feature is essential for ensuring business continuity, mitigating risks and building strategic partnerships.
In today’s fast-changing procurement landscape, Know Your Supplier (KYS) is essential for ensuring business continuity, mitigating risks, and building strategic partnerships. This is particularly crucial in regions like Africa, where supplier data often remains fragmented and manually managed, highlighting the need for robust, scalable solutions.
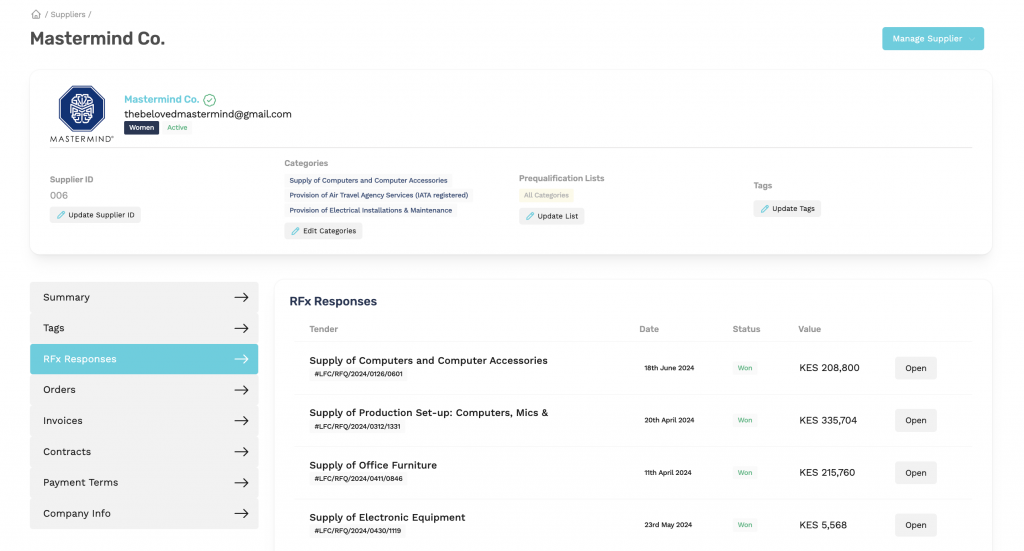
Scale’s Supplier Master Table captures and tracks all relevant supplier data points, providing buyers with an unparalleled view of their suppliers.
Below, we explore why each data category is important, with examples for context, and highlight the specific information Scale collects to ensure procurement excellence.
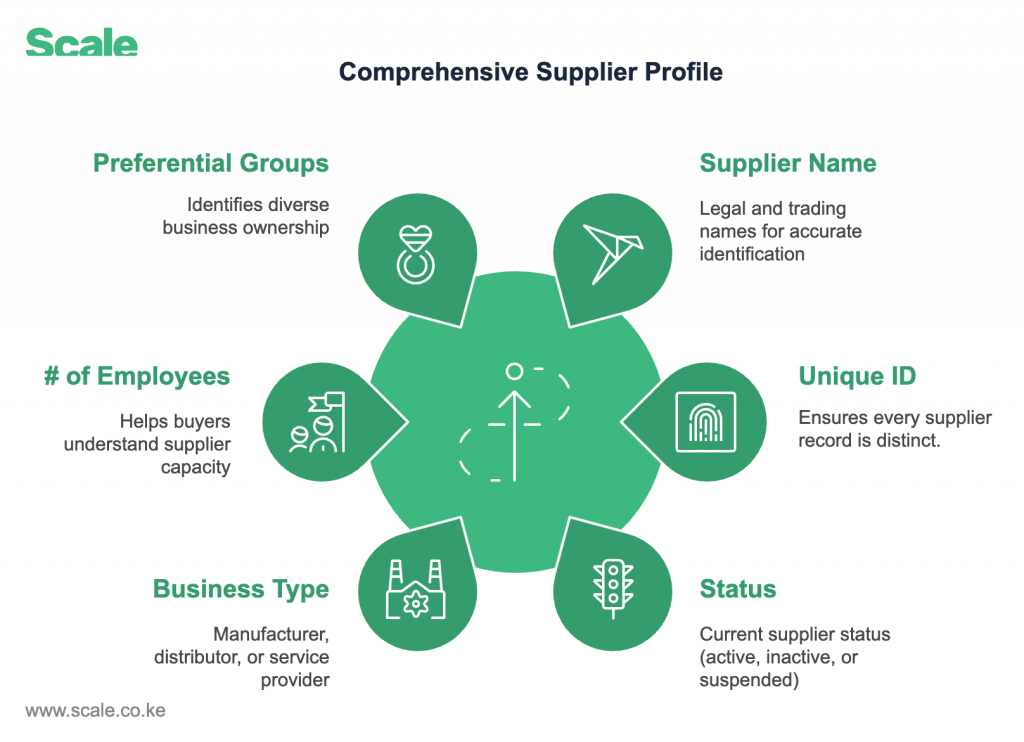
1. General Information: The Foundation of Supplier Management
Why It Matters:
Accurate supplier information is the backbone of effective procurement. KYS (Know Your Supplier) ensures clarity, prevents misunderstandings, and allows for efficient record-keeping and operations.
What Scale Collects:
- Supplier Name: Legal and trading names for accurate identification.
- Business Registration Number: Verification of the entity’s legal registration.
- Legal Structure: LTD, LLC, Partnership, Sole proprietorship, etc.
- Business Identification Numbers: Tax ID for compliance.
- Unique ID: Ensures every supplier record is distinct.
- Status: Current supplier status (active, inactive, or suspended).
- Business Type: Manufacturer, distributor, or service provider.
- Number of Employees: Helps buyers understand supplier capacity.
- Preferential Groups: Identifies Women, Youth, PWD, Local Contractors, or Citizen Contractors.
- Addresses: Both physical and postal.
- Primary & Alternative Contacts: Names, titles, and direct communication details.
- Categories: Products or services offered by the supplier.
- Payment Terms: Flexible options like Net 30 or Net 60.
- Parent Company/Subsidiaries: Provides insights into corporate relationships.
- Geographical Reach: Operational coverage (county, national, or international).
Example: A construction firm sourcing cement in Kenya benefits from knowing if a supplier’s reach extends to counties like Turkana or Samburu, ensuring on-time delivery to remote project sites.
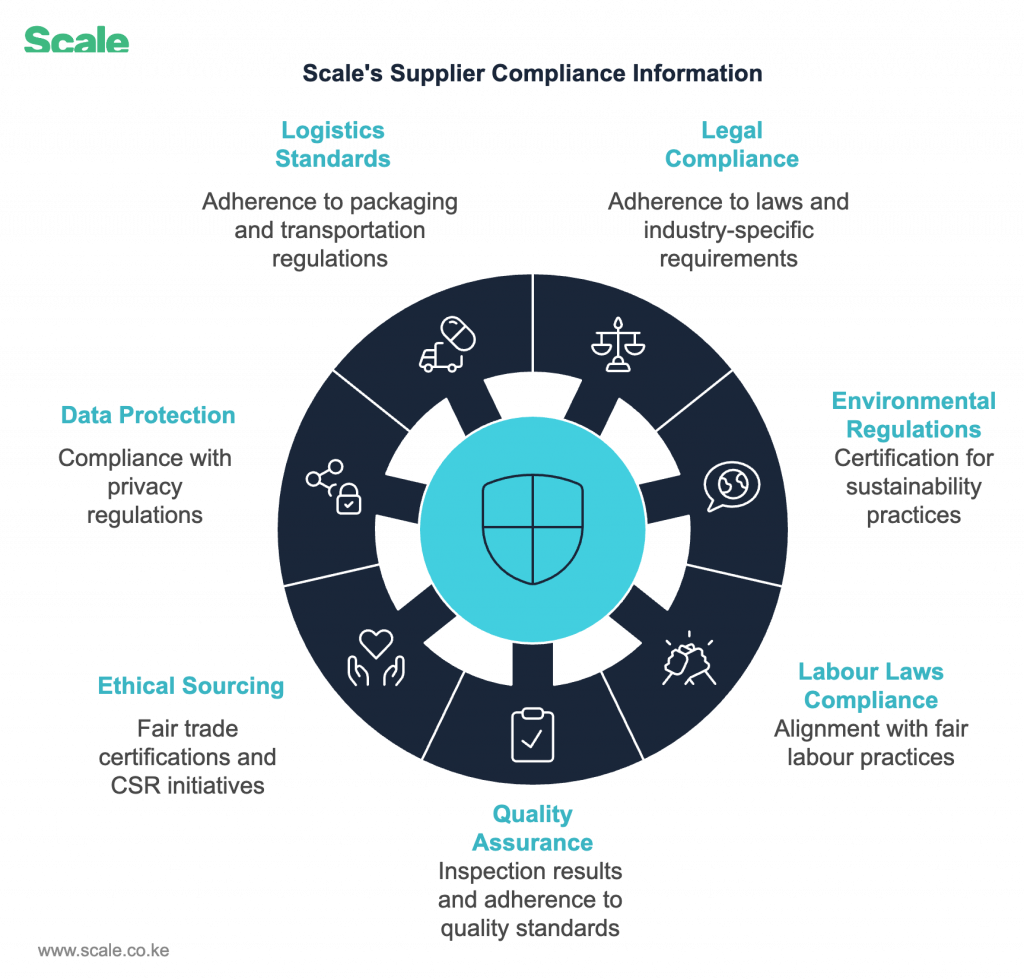
2. Compliance Information: Mitigating Risks
Why It Matters:
Ensuring suppliers comply with local and international regulations protects buyers from legal penalties and operational disruptions.
What Scale Collects:
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to laws and industry-specific requirements.
- Environmental Regulations: Certification for sustainability practices.
- Labour Laws Compliance: Alignment with fair labour practices.
- Quality Assurance: Inspection results and adherence to quality standards.
- Ethical Sourcing: Fair trade certifications and CSR initiatives.
- Data Protection and Cybersecurity: Compliance with privacy regulations like Kenya’s Data Protection Act.
- Logistics and Packaging Standards: Adherence to packaging and transportation regulations.
Example: A Kenyan food processing company can safeguard its reputation and consumer health by verifying that its input suppliers adhere to stringent manufacturing and quality standards, ensuring safe and compliant materials for consumables.
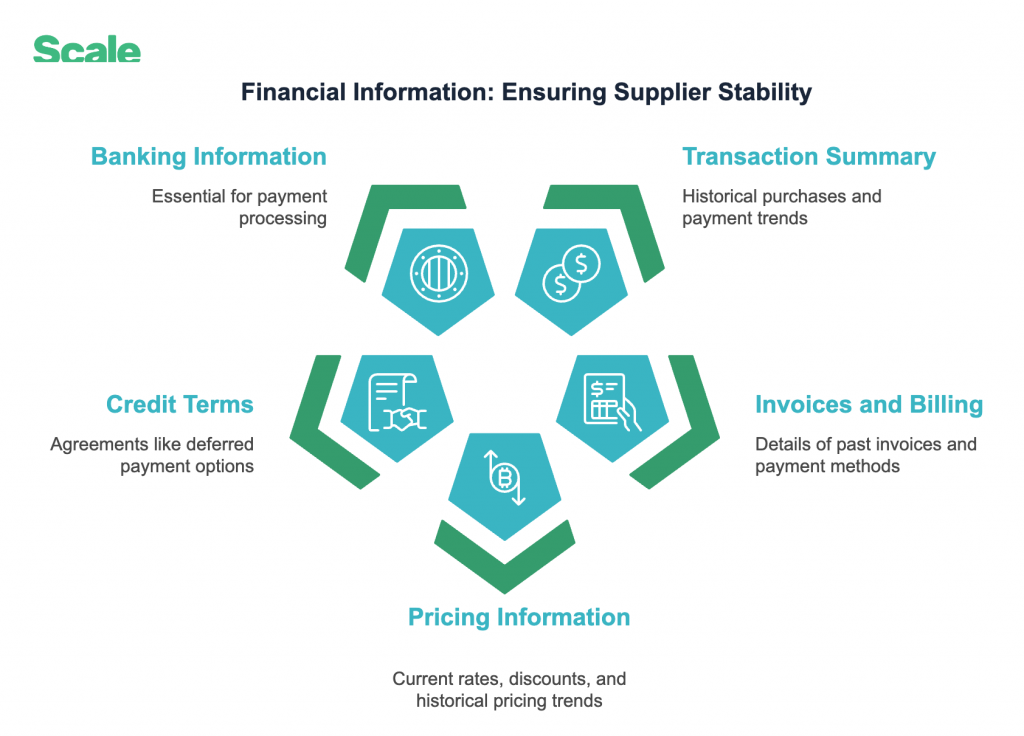
3. Financial Information: Ensuring Supplier Stability
Why It Matters:
Financial health is a key indicator of a supplier’s reliability and capacity to meet obligations.
What Scale Collects:
- Transaction Summary: Historical purchases and payment trends.
- Invoices and Billing Information: Details of past invoices and payment methods.
- Pricing Information: Current rates, discounts, and historical pricing trends.
- Credit Terms and Limits: Agreements like deferred payment options.
- Banking Information: Essential for payment processing.
- Currencies Accepted: Ensures alignment for international trade.
Example: A logistics firm in Nairobi can avoid disruptions by assessing a fuel supplier’s financial health through lines of credit, financial statements and audited financial reports.
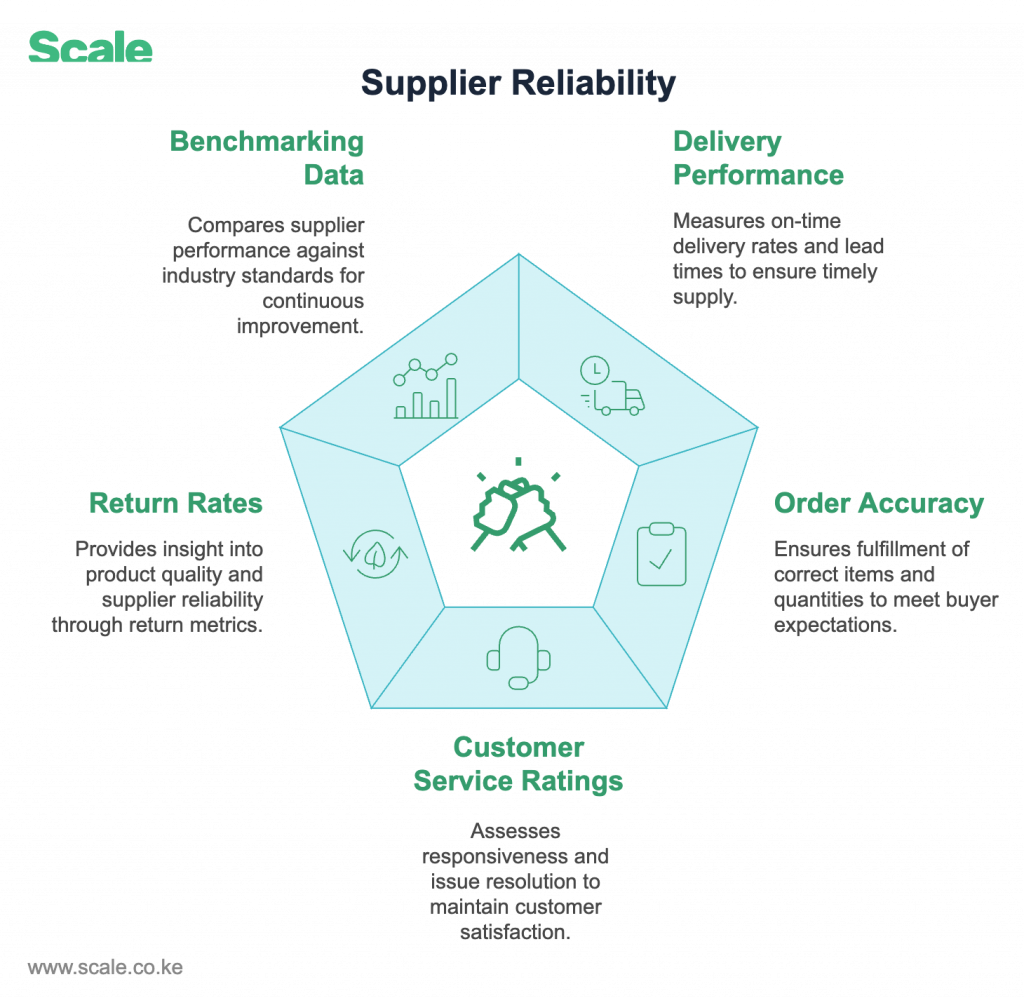
4. Performance Metrics: Measuring Supplier Reliability
Why It Matters:
Tracking performance ensures suppliers deliver on their commitments and helps buyers make data-driven decisions.
What Scale Collects:
- Delivery Performance: On-time delivery rates and lead times.
- Order Accuracy: Fulfillment of correct items and quantities.
- Customer Service Ratings: Responsiveness and issue resolution.
- Return/Refund Rates: Insight into quality and reliability.
- Benchmarking Data: Comparison against industry standards.
Example: A healthcare provider sourcing medical supplies can track on-time delivery rates to ensure uninterrupted patient care across counties.
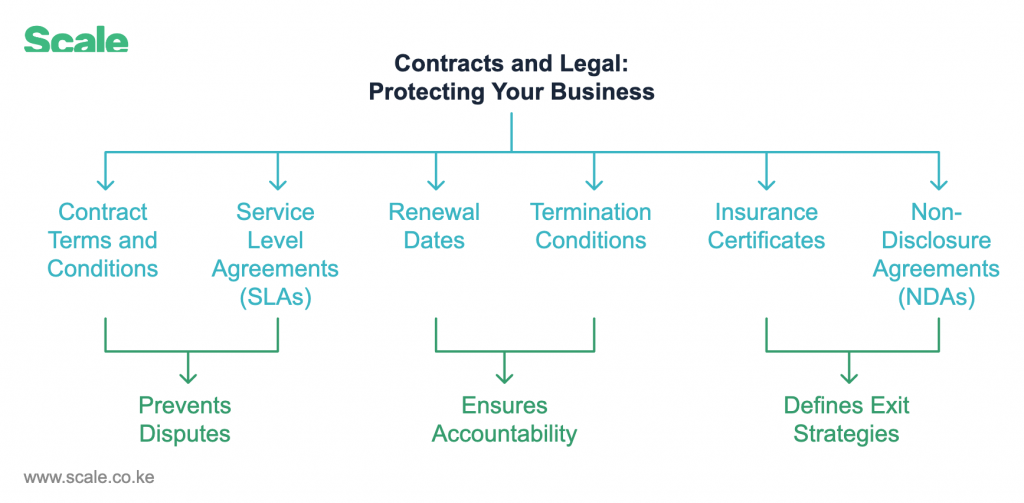
5. Contracts and Legal: Protecting Your Business
Why It Matters:
Clear documentation prevents disputes, ensures accountability, and defines exit strategies.
What Scale Collects:
- Contract Terms and Conditions: Comprehensive details of agreements.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Clear performance benchmarks.
- Renewal Dates: Automatic reminders for contract renewals.
- Termination Conditions: Defined pathways to terminate agreements.
- Insurance Certificates: Ensures suppliers are adequately insured.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): Protection for sensitive data.
Example: A Nairobi-based IT firm procuring software licenses can track SLAs to ensure technical support and guaranteed uptime.
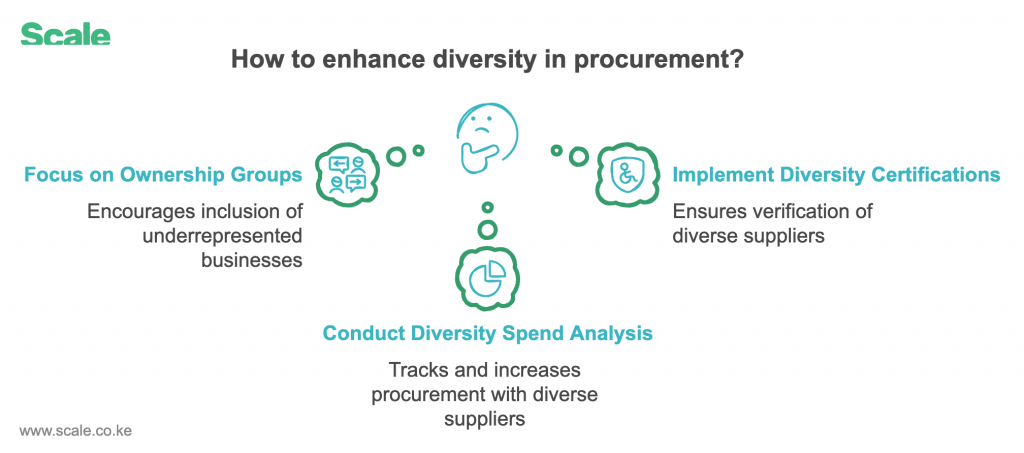
6. Diversity and Inclusion: Supporting Broader Goals
Why It Matters:
Diversity in procurement supports corporate social responsibility, aligns with local regulations, and fosters economic development.
What Scale Collects:
- Ownership Groups: Women-owned, youth-owned, or disability-inclusive businesses.
- Diversity Certifications: Verification of diverse supplier qualifications.
- Diversity Spend Analysis: Tracks percentage of procurement allocated to diverse suppliers.
Example: A Nairobi Stock Exchange-listed buyer in Kenya can prioritize women-owned businesses to align with its affirmative action policies.
7. Sustainability and CSR: Future-Proofing Supply Chains
Why It Matters:
Buyers can align their procurement strategies with sustainability goals, reducing risks and enhancing their brand reputation.
What Scale Collects:
- Sustainability Certifications: LEED, Fair Trade, or equivalent standards.
- Carbon Footprint Data: Measures supplier environmental impact.
- CSR Initiatives: Contributions to community and social programs.
Example: A coffee exporter can work with suppliers certified by Rainforest Alliance, ensuring compliance with sustainable farming practices.
8. Technology and Innovation: Staying Ahead
Why It Matters:
Suppliers leveraging technology are often more efficient and adaptable, ensuring better service delivery.
What Scale Collects:
- Technological Capabilities: Use of ERP, CRM, and other digital tools.
- R&D Investments: Percentage of revenue allocated to innovation.
- Innovation Track Record: Patents and product development timelines.
Example: A retail chain benefits from suppliers with advanced logistics platforms for real-time tracking and inventory accuracy.
9. Feedback and Reviews: Driving Continuous Improvement
Why It Matters:
Ongoing evaluations help buyers identify and address issues early while rewarding high-performing suppliers.
What Scale Collects:
- Internal Feedback: Insight from procurement teams.
- Customer Reviews: Ratings and testimonials from other clients.
- Audit Results: Third-party assessments of supplier performance.
Example: A hospitality group sourcing organic produce uses supplier evaluations to compare vendors on quality, delivery, and pricing.
Why Scale is the Ideal Solution for “Know Your Supplier”
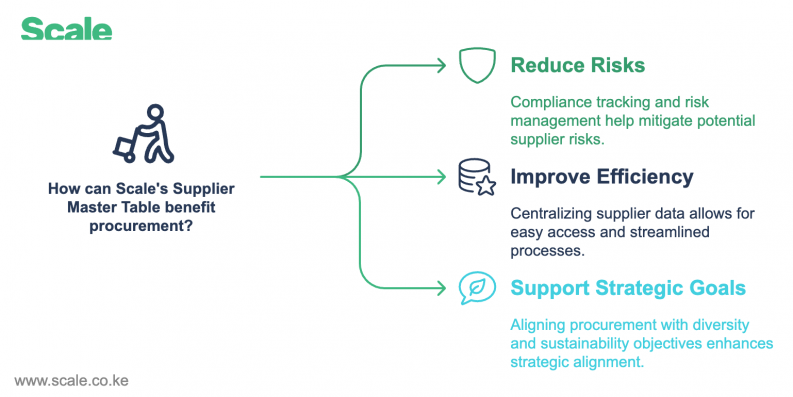
Scale provides a holistic supplier management solution by collecting and organizing data across these categories. The Supplier Master Table helps procurement teams:
- Reduce Risks: Through compliance tracking and risk management.
- Improve Efficiency: By centralizing supplier data for easy access.
- Support Strategic Goals: Aligning procurement with diversity and sustainability objectives.
In Kenya and Africa, procurement teams face unique challenges, from regulatory complexities to diverse supplier landscapes. Scale’s Supplier Master Table addresses these challenges with unparalleled data collection and actionable insights, empowering buyers to make informed decisions and build sustainable partnerships.
Ready to redefine your procurement process? Start with Scale, know your supplier and experience data-driven supplier management like never before!






